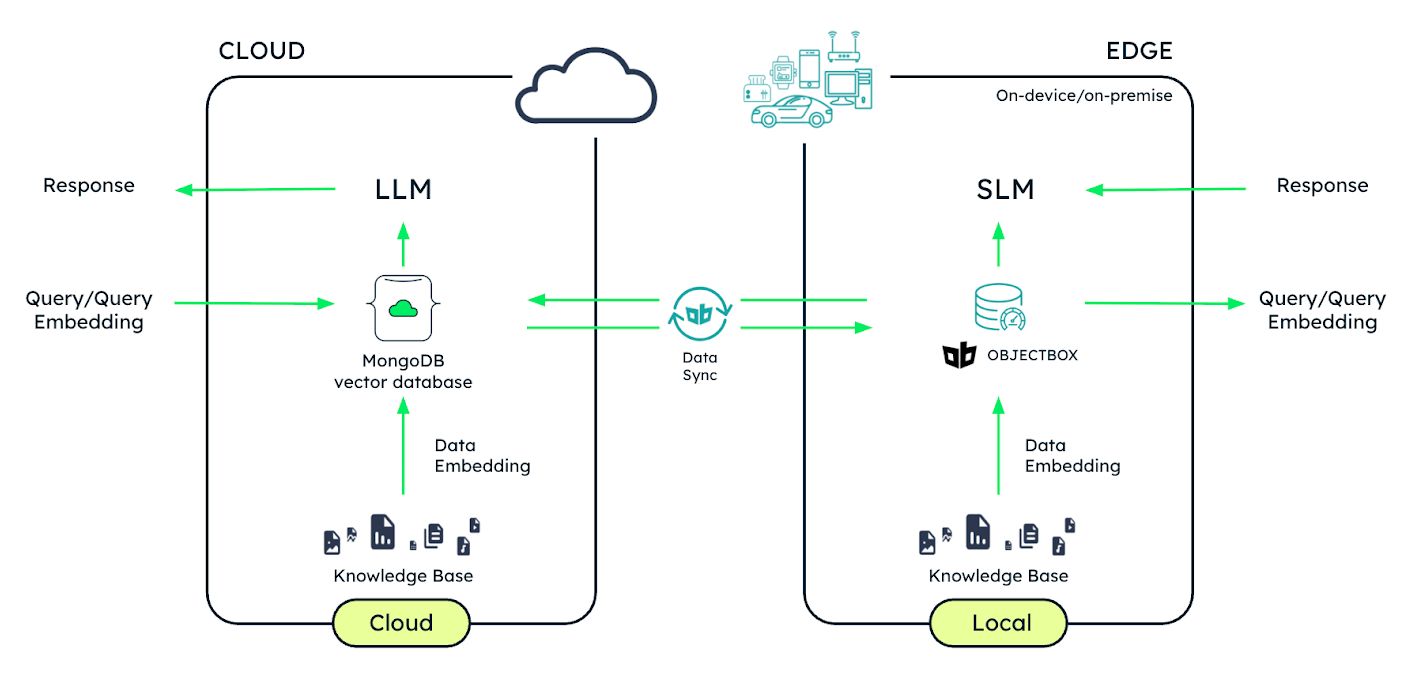
AI is currently undergoing a shift, from massive centralized models to distributed, real-world deployments. While the cloud remains the foundation for large-scale AI training and analytics, AI’s next evolution lies at the edge—where data is created, where decisions require instant action, and where connectivity cannot be guaranteed.
At MongoDB, we are committed to helping organizations build intelligent applications that span cloud and edge environments seamlessly. That’s why we are excited to highlight our work with ObjectBox, a lightweight, high-performance on-device database and sync solution purpose-built for edge AI and offline-first applications.
Together, MongoDB and ObjectBox are making it easier for developers to build hybrid architectures that deliver fast, private, and resilient AI experiences across devices and environments.
Figure 1. Example cloud-edge AI setup.
ObjectBox: A purpose-built database for the edge
Founded by Markus Junginger and Dr. Vivien Dollinger, ObjectBox was designed specifically to support edge computing and offline-first use cases. At its core, ObjectBox’s design prioritizes efficiency (including speed, privacy, battery use, and memory consumption) and ease of development.
This strong foundation makes ObjectBox particularly well-suited for next-generation applications that need to run reliably in edge environments—whether on a factory floor, in a retail store, or through a remote healthcare device. ObjectBox empowers developers to build responsive, privacy-conscious applications that work even when connectivity is limited or unavailable.
The platform includes the following features:
A fast, local vector database that stores data directly on devices, supporting on-device AI and local vector search.
Built-in data sync, which keeps data consistent across devices even when offline, and now integrates directly with MongoDB.
Multi-language support, including support for C++, Swift, Flutter, Python, Go, Java, and Kotlin, makes ObjectBox accessible to developers across ecosystems.
These features make ObjectBox an ideal solution for building intelligent applications that run reliably at the edge. This includes a wide range of devices—from smartphones and industrial sensors to automotive ECUs and point-of-sale (POS) devices.
Edge to cloud data sync: The MongoDB Atlas native connector
ObjectBox's new MongoDB Sync Connector combines local-first edge processing with centralized cloud intelligence (i.e., hybrid AI).
This is increasingly important as organizations seek to process data closer to where it is generated—at the edge—while still benefiting from the power and scalability of the cloud. Managing this dual environment efficiently is key to unlocking performance, resilience, and real-time insights.
Developers can now use ObjectBox for real-time, low-latency operations on edge devices while syncing relevant data to MongoDB Atlas, enabling organizations to achieve:
Long-term storage
Centralized dashboards and analytics
AI model retraining
Cloud-based coordination and automation
This hybrid architecture aligns with how modern applications are being built—distributing intelligence where it makes the most sense.
Figure 2. Central Sync for ObjectBox and MongoDB Atlas.
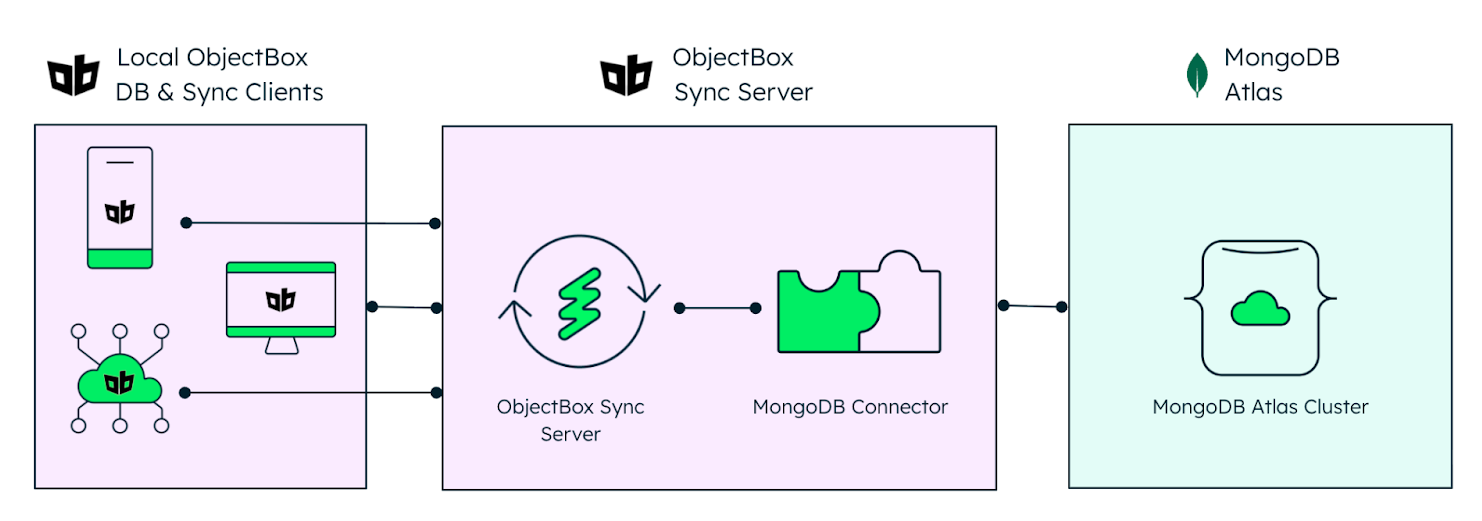
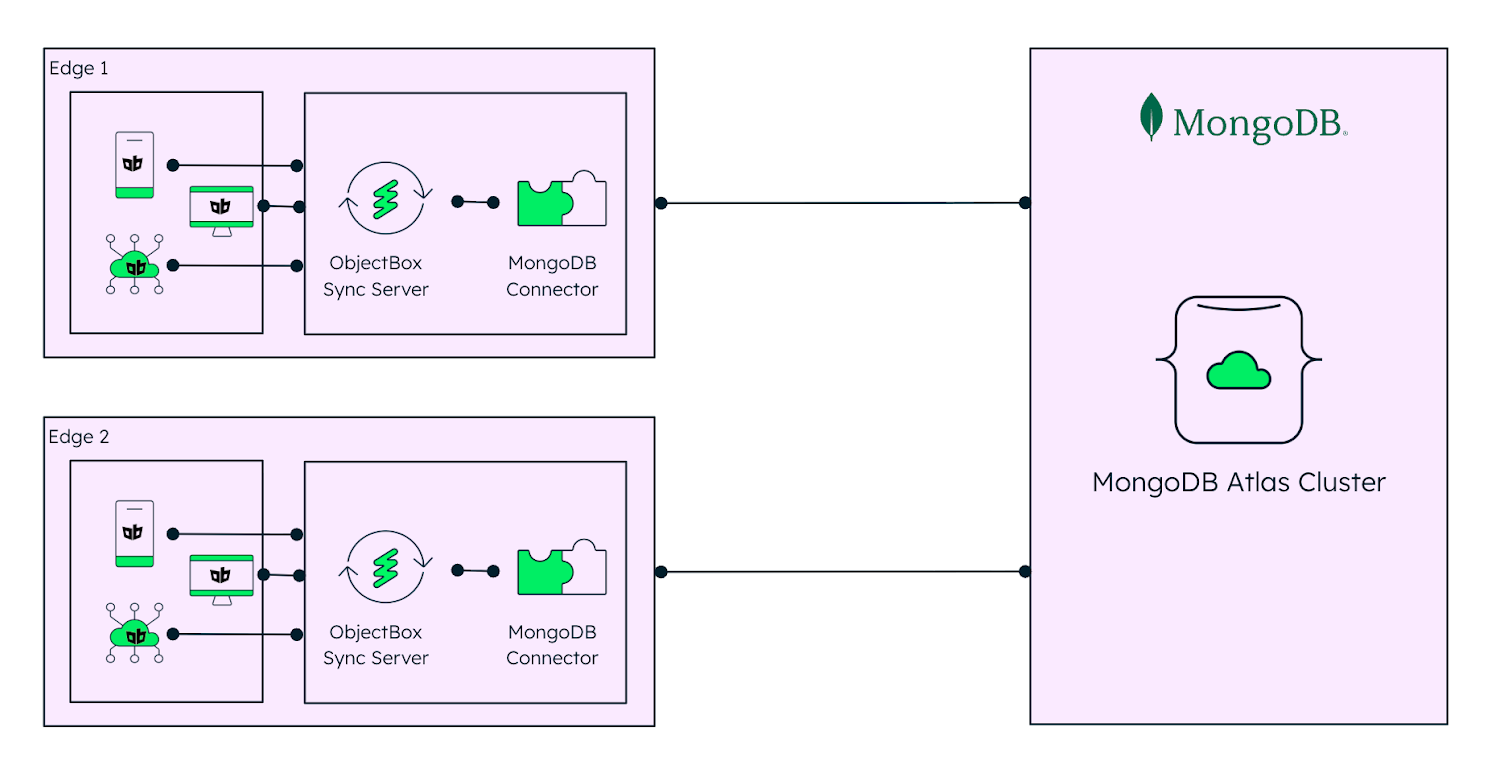
Figure 3. Edge setup for ObjectBox and MongoDB Atlas.
Bringing AI to the edge isn’t just about performance. It is also about privacy, sustainability, and user experience. By processing data locally:
Privacy is enhanced—sensitive information stays on the device.
Latency is reduced—actions can be taken instantly.
Bandwidth usage drops—lowering costs and improving efficiency.
Battery and CPU use are optimized—extending the life of edge devices.
This aligns with MongoDB’s commitment to empowering developers to build intelligent, resilient, and user-centric applications—wherever they need.
Real-world use cases
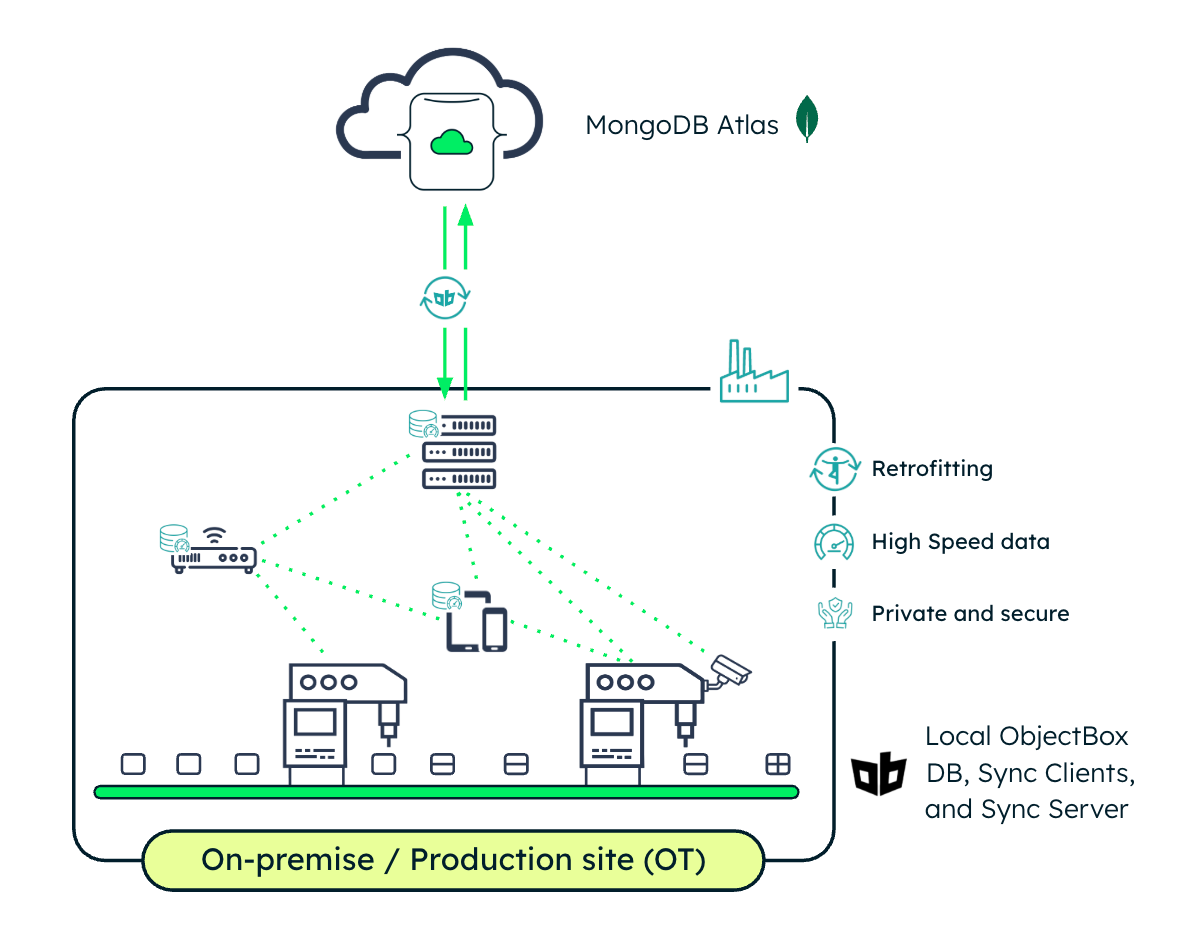
Industrial IoT
Industrial IoT (IIoT) is a prime example of where edge and cloud must work together. On a modern factory floor, everything from low-frequency brownfield devices to high-frequency greenfield machines generates vast amounts of data.
Data generated include vibration levels, temperature readings, pressure changes, and machine runtimes. In short, the sort of data that often needs to be processed locally to monitor systems in real time and to trigger alerts when anomalies or threshold breaches occur.
With ObjectBox running on device, this critical operational data can be captured, analyzed, and used onsite and within AI applications immediately, even with limited or no connectivity. ObjectBox is designed for efficient, high-throughput I/O, enabling real-time processing of high-frequency data streams even on resource-constrained edge devices.
It supports a broad range of data types—from objects and time series data, to tree structures (e.g., UMATI) and vector embeddings—with a lightweight database (typically only a few MB in size). This makes it well-suited for production deployments that need to integrate modern AI and edge workloads with legacy systems and heterogeneous hardware, typical for the manufacturing industry.
The ObjectBox Sync Server can run on almost any device, enabling fast, reliable, and secure offline data synchronization across the shop floor. Paired with the MongoDB Sync Connector, the most relevant insights can then be synced to the cloud, where they can be aggregated, enriched with AI models, and stored for long-term analysis (like anomaly detection or RUL models).
This hybrid architecture enables advanced use cases such as predictive maintenance, where historical records, live equipment data, and machine learning models are combined to forecast potential failures before they happen. (For more details, explore our Predictive Maintenance solutions library.)
With this architecture, the system provides:
Real-time responsiveness on the shop floor
Centralized analytics and cross-site dashboards at cloud scale
Support for predictive maintenance workflows in offline or intermittently connected environments
Unified data access across heterogeneous data sources, from individual sensors to full production lines
By combining low-latency edge processing with centralized intelligence, developers and operators gain visibility into how equipment is performing from the health of a single machine, to trends across an entire fleet or factory network—without compromising performance or reliability.
Figure 4. Industrial IoT.
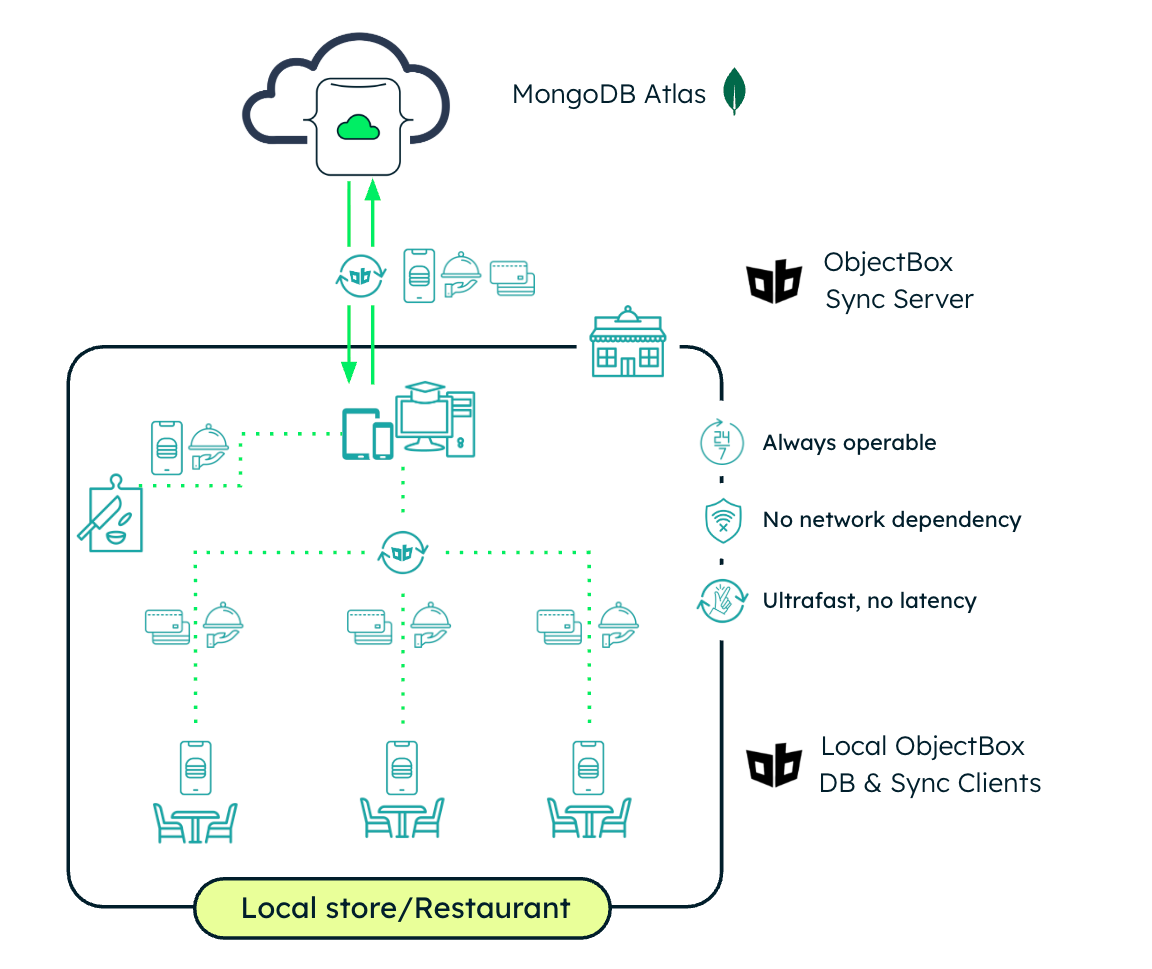
Point-of-sale systems
Point-of-sale (POS) systems—such as those used in restaurants—are another strong fit for edge AI and hybrid architectures. During peak dining hours, cashiers and servers need instant, reliable access to menus, order histories, and payment processing—even if their internet connection is unstable or drops.
With ObjectBox’s offline-first, on-device database, restaurants can process real-time transactions, track inventory, and personalize customer experiences with local AI directly at the POS terminal. This helps store owners avoid service disruptions or lost sales.
With MongoDB Sync Connector, relevant data (like sales trends, customer preferences, and stock levels) syncs to MongoDB Atlas. This enables restaurant managers to run centralized dashboards, perform demand forecasting, and train AI models that optimize staffing, menu design, and supply chain planning.
In summary, this hybrid POS architecture of local-first responsiveness and cloud-powered insights ensures:
Seamless customer experiences without downtime
Accurate, up-to-date data whenever needed
Scalable, resilient operations across multiple restaurant locations
Figure 5. Point-of-sale systems.
What’s next
With the release of ObjectBox 5.0 and its new MongoDB Connector, ObjectBox has taken a major step toward simplifying user‑specific data sync at the edge. Together, MongoDB and ObjectBox offer a modern foundation for building intelligent, distributed applications that run reliably from device to cloud. This partnership makes it easier than ever to pair low‑latency edge data processing with the flexibility, security, and global reach of MongoDB Atlas.
Next Steps
Developers can begin exploring ObjectBox and MongoDB together by:
Signing up for a Data Sync Trial, including the MongoDB Sync Connector.
Building local-first applications with MongoDB Atlas.